For most of the poverty-related infectious diseases, which are a major obstacle to the sustainable development of sub-Saharan Africa, there is paucity of effective, safe, suitable and affordable medical treatments. Drugs tailored to the special circumstances of the developing countries and populations at high risk, either do not exist or are limited. Additionally, co-infections with several pathogens are frequent in sub-Saharan Africa and represent an important public health problem in many areas. Diseases progress faster or with complications which results in increased mortality and morbidity. Co-infections can also result in unique challenges to treatment and prevention of diseases, for example through increased drug toxicities and/or changes in the efficacy of interventions.
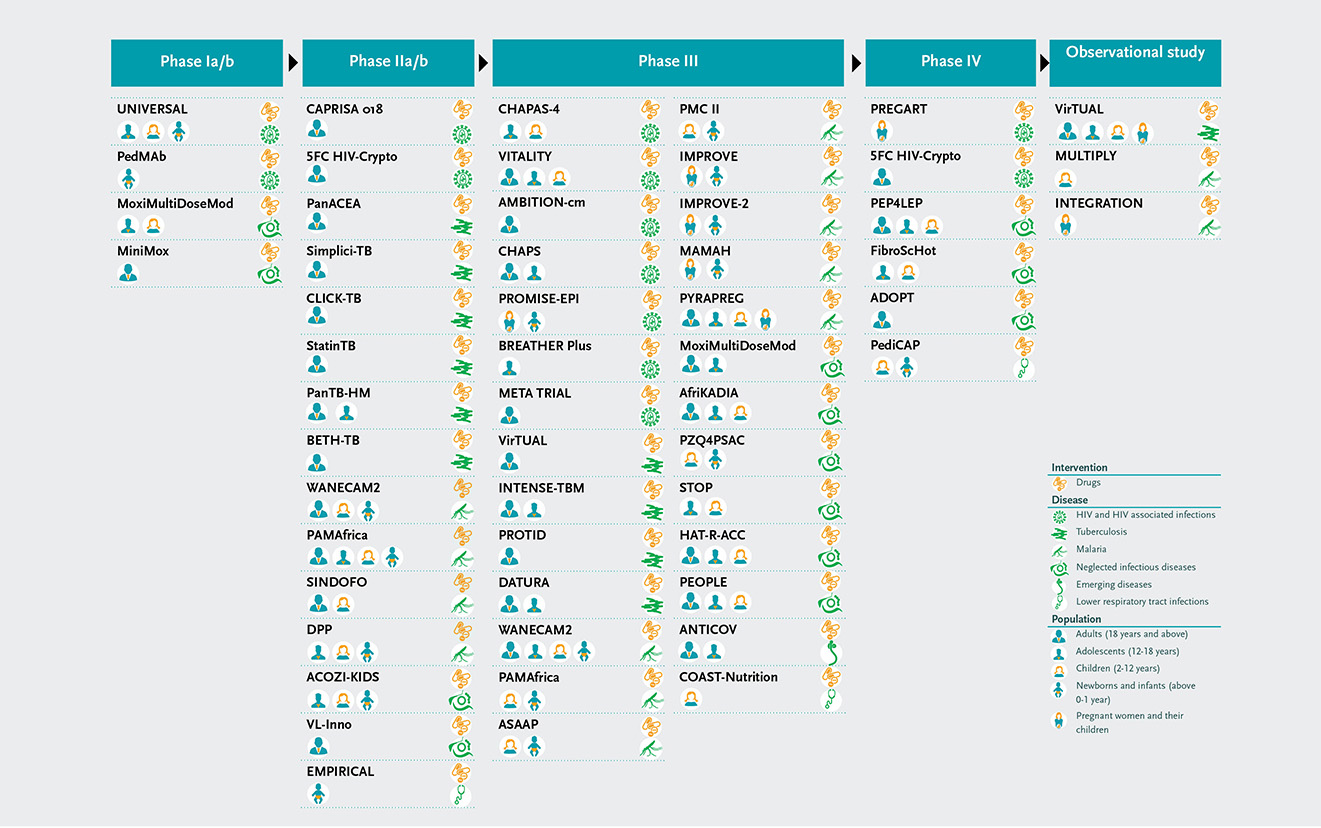
By end of 2021, EDCTP supported 51 collaborative clinical research and clinical trials that aim to evaluate new or improved drugs or drug regimens in humans or aim to optimise the efficacy and use of existing therapeutics for poverty-related diseases (including coinfections). These projects account for € 282.01 million in funding.
EDCTP portfolio: drugs
Collaborative clinical trials and clinical research (2014-2021)